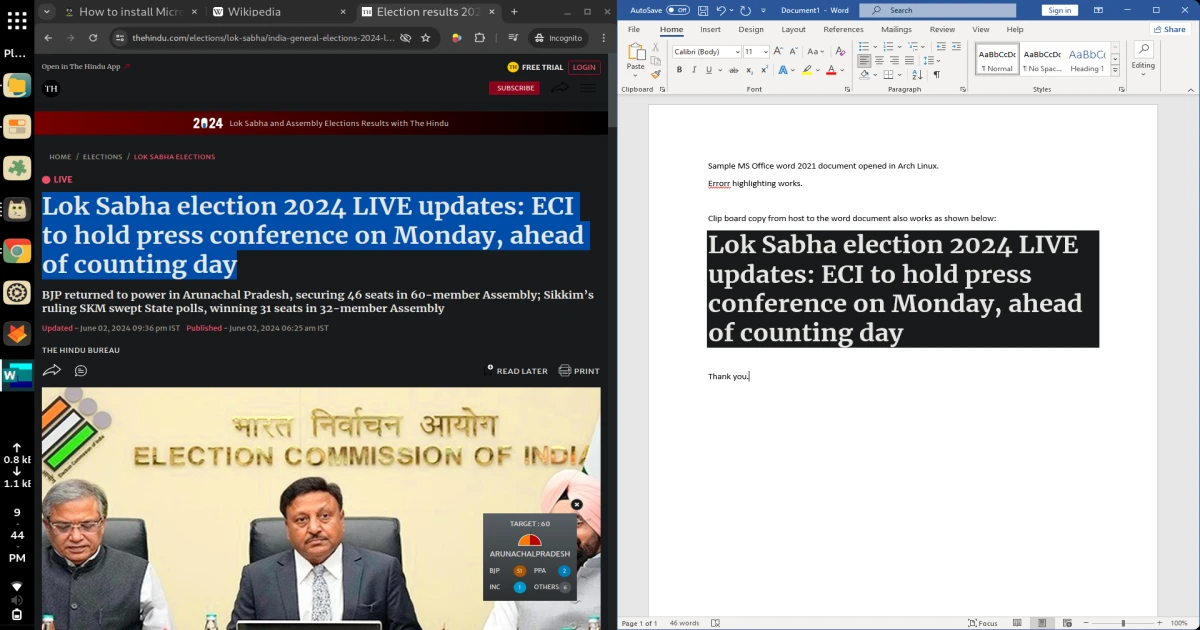
How to install Microsoft Office 2007/ 2010/ 2016/ 2021/ 365 or any version on Linux
A post regarding installing MS Office on Alma Linux or RHEL based OS is available at https://wxguy.in/posts/install-ms-office-any-version-on-rhel-alma-linux-based-distros. You may find it interesting and useful as there are not many tutorials available on this topic.
Requirement of Microsoft Office
Undoubtedly, Microsoft Office is one of the most popular and most widely used Office suites in the world. Especially, names such as Word, Powerpoint and Excel have become synonymous with office applications/ suits. Based on my experience, I can tell that a new user who shifted to Linux would immediately search for procedures to install Microsoft Office on a Linux OS. As with other software, there are many native alternatives available for Linux. However, the biggest issue here is the compatibility of file types. The Word files or presentations created in Microsoft Office would never open properly in other Office suites, including the de-facto Office suite ‘Libre Office’. The myriad of formulas and options available in Excel will never come in other Office suites anytime soon. Therefore, it is a natural choice for users to switch between Microsoft Windows and Linux Desktop for simply using this great piece of software.
Options available to Install Microsoft Office on Linux
When searching online for installing MS Office on Linux Desktop, most of the tutorials would tell you to follow one of the following methods:-
Use alternate native software such as Libre Office, WPS Office, Open Office etc.
Use wine to install MS Office.
Use PlayonLinux which under-the-hood uses wine.
Use Paid software for better compatibility such as crossover which is again the improved version of wine.
Use Windows Virtual Machine inside Linux Desktop and use it whenever required.
or finally
- Install Windows OS alongside Linux and boot into Windows whenever required.
When you follow any one of the methods listed above, either you will end up using an older version of MS Office or you will still use the software that is not fully compatible with MS Office (except using MS Office directly inside Windows). I have tested all the methods and the best solution I found is the procedure listed in subsequent paragraphs.
Winapps for Native Windows Software (kind-of) on Linux
So what is so fuzz about Winapps? It is a community software which offers one of the virtualisation solutions to run any Windows applications as if they are installed inside a Linux Desktop. It uses Windows Virtual Machine to install the software and FreeRDP to access this software from Linux. The beauty of this application is the native integration of the file manager right-click option to open and specify the mime type to open in Windows software.
When I heard about this software two years ago in 2022, I tried it many times and it always gave me some sort of issues which forced me to uninstall. The application was initially developed at https://github.com/Fmstrat/winapps. However, the repo did not receive an update for a long time. Therefore, the project was forked and maintained by the community at https://github.com/winapps-org/winapps. Recently, I gave Winapps software again a try and did not encounter an issue. I also found it to be too good for running day-to-day utility. Right now, I have installed MS Office 2021 and the application works flawlessly on my Arch Linux desktop.
I will be writing more about the technical know-how on installing and configuring winapps for using MS Office 20xx/ 365 in this blog post. There are many steps involved in configuring the software correctly. Read and execute the commands carefully.
System Configuration
I will be covering this tutorial on Arch Linux as it is the only desktop I use nowadays. If you use any other desktop, you must install equivalent commands on your own. Here is my system configuration:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
neofetch
-` sundar@archlinux
.o+` ----------------
`ooo/ OS: Arch Linux x86_64
`+oooo: Host: TravelMate P214-53 V1.47
`+oooooo: Kernel: 6.6.32-1-lts
-+oooooo+: Uptime: 1 hour, 48 mins
`/:-:++oooo+: Packages: 1691 (pacman), 15 (flatpak)
`/++++/+++++++: Shell: zsh 5.9
`/++++++++++++++: Resolution: 1920x1080
`/+++ooooooooooooo/` DE: GNOME 46.2
./ooosssso++osssssso+` WM: Mutter
.oossssso-````/ossssss+` WM Theme: Adwaita
-osssssso. :ssssssso. Theme: Adwaita [GTK2/3]
:osssssss/ osssso+++. Icons: Adwaita [GTK2/3]
/ossssssss/ +ssssooo/- Terminal: kitty
`/ossssso+/:- -:/+osssso+- CPU: 11th Gen Intel i7-1165G7 (8) @ 4.700GHz
`+sso+:-` `.-/+oso: GPU: Intel TigerLake-LP GT2 [Iris Xe Graphics]
`++:. `-/+/ Memory: 11065MiB / 15775MiB
.` `/
Install Necessary Software
The procedure we are going to follow uses docker for installing and running Windows 11 in the background. I use paru helper software for installing packages. Please whatever package manager is comfortable to you. Install all the necessary packages:
1
paru -Syu --needed -y curl dialog freerdp git iproute2 libnotify gnu-netcat docker docker-compose
Check if docker is installed correctly using following command:
1
docker --version
and docker-compose using following command:
1
docker-compose --version
Add docker to user group:
1
sudo usermod -a -G docker $USER
Start the docker using:
1
sudo systemctl start docker
or
1
sudo dockerd
Enable docker services using:
1
sudo systemctl enable docker
Ensure that docker is running using following command:
1
systemctl status docker.service
this should show the following output:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
● docker.service - Docker Application Container Engine
Loaded: loaded (
/usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service; enabled; preset:
disabled)
Active: active (running) since Sun 2025-02-09 15:06:20 UTC; 42s
ago
Invocation: 29275868b7db421f8e199af105b7b85e
TriggeredBy: ● docker.socket
Docs: https://docs.docker.com
Main PID: 639 (dockerd)
Tasks: 13
Memory: 86.2M (peak: 88.4M)
CPU: 290ms
CGroup: /system.slice/docker.service
└─639 /usr/bin/dockerd -H fd:// --containerd=/run/conta
inerd/containerd.sock
Install Windows OS Using Docker
Once the system software is installed and configured, we need to install Windows Virtual Machine on the host OS. We will be using the docker for this purpose. The main advantage of this method is to install the Windows OS without user intervention and run it in the background. It also does not require the user to have a Windows OS ISO file as it would automatically download as part of the installation process. Before we start installing the Windows OS, we need to clone the winapps repo. I am cloning it in ~/ directory.
1
2
cd ~/
git clone https://github.com/winapps-org/winapps
Move to the winapps directory and ensure that compose.yaml file exists in the same directory.
1
2
cd winapps
ls com*
Which should show the following output:
1
compose.yaml
All the details about Windows OS are saved in the above *.yaml file. Sample compose.yaml file will is shown below:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
# For documentation, FAQ, additional configuration options and technical help, visit: https://github.com/dockur/windows
name: "winapps" # Docker Compose Project Name.
volumes:
# Create Volume 'data'.
# Located @ '/var/lib/docker/volumes/winapps_data/_data' (Docker).
# Located @ '/var/lib/containers/storage/volumes/winapps_data/_data' or '~/.local/share/containers/storage/volumes/winapps_data/_data' (Podman).
data:
services:
windows:
image: ghcr.io/dockur/windows:latest
container_name: WinApps # Created Docker VM Name.
environment:
# Version of Windows to configure. For valid options, visit:
# https://github.com/dockur/windows?tab=readme-ov-file#how-do-i-select-the-windows-version
# https://github.com/dockur/windows?tab=readme-ov-file#how-do-i-install-a-custom-image
VERSION: "tiny11"
RAM_SIZE: "4G" # RAM allocated to the Windows VM.
CPU_CORES: "4" # CPU cores allocated to the Windows VM.
DISK_SIZE: "64G" # Size of the primary hard disk.
#DISK2_SIZE: "32G" # Uncomment to add an additional hard disk to the Windows VM. Ensure it is mounted as a volume below.
USERNAME: "sundar" # Edit here to set a custom Windows username. The default is 'MyWindowsUser'.
PASSWORD: "Pa$$w0rd" # Edit here to set a password for the Windows user. The default is 'MyWindowsPassword'.
HOME: "${HOME}" # Set path to Linux user home folder.
privileged: true # Grant the Windows VM extended privileges.
ports:
- 8006:8006 # Map '8006' on Linux host to '8006' on Windows VM --> For VNC Web Interface @ http://127.0.0.1:8006.
- 3389:3389/tcp # Map '3389' on Linux host to '3389' on Windows VM --> For Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP).
- 3389:3389/udp # Map '3389' on Linux host to '3389' on Windows VM --> For Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP).
stop_grace_period: 120s # Wait 120 seconds before sending SIGTERM when attempting to shut down the Windows VM.
restart: on-failure # Restart the Windows VM if the exit code indicates an error.
volumes:
- data:/storage # Mount volume 'data' to use as Windows 'C:' drive.
- ${HOME}:/shared # Mount Linux user home directory @ '\\host.lan\Data'.
#- /path/to/second/hard/disk:/storage2 # Uncomment to mount the second hard disk within the Windows VM. Ensure 'DISK2_SIZE' is specified above.
- ./oem:/oem # Enables automatic post-install execution of 'oem/install.bat', applying Windows registry modifications contained within 'oem/RDPApps.reg'.
#- /path/to/windows/install/media.iso:/custom.iso # Uncomment to use a custom Windows ISO. If specified, 'VERSION' (e.g. 'tiny11') will be ignored.
devices:
- /dev/kvm # Enable KVM.
#- /dev/sdX:/disk1 # Uncomment to mount a disk directly within the Windows VM (Note: 'disk1' will be mounted as the main drive. THIS DISK WILL BE FORMATTED BY DOCKER).
#- /dev/sdY:/disk2 # Uncomment to mount a disk directly within the Windows VM (Note: 'disk2' and higher will be mounted as secondary drives. THIS DISK WILL NOT BE FORMATTED).
Edit the above compose.yaml file to change username and password of your choice. In my case, I have changed USERNAME to sundar and PASSWORD to Pa$$w0rd.
We will be using the above information to tell the docker-compose command to install the Windows OS with all the specifications listed above. You must edit the file content depending on your hardware and liking. The compose.yaml is a yaml file. In our case, we will be installing the Windows 11 Tiny version to save space and resources. It is easy to understand the terminologies of the above file. You can always refer to https://github.com/dockur/windows for further tweaking the file content. Once saved, you can run the below command to install the Windows OS:
1
docker compose --file ~/winapps/compose.yaml up
This should produce following output:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
[+] Running 7/7
✔ windows Pulled 26.9s
✔ 7890380f2910 Pull complete 21.2s
✔ c66652c32996 Pull complete 24.2s
✔ 2634bc5d9134 Pull complete 24.3s
✔ d7f53ee8739a Pull complete 24.4s
✔ 3c169cf00d7d Pull complete 24.5s
✔ aac9e36b2ca2 Pull complete 24.6s
[+] Running 3/3
✔ Network winapps_default Created 0.1s
✔ Volume "winapps_data" Created 0.0s
✔ Container WinApps Created 0.1s
Attaching to WinApps
WinApps | ❯ Starting Windows for Docker v4.10...
WinApps | ❯ For support visit https://github.com/dockur/windows
WinApps | ❯ CPU: Intel Core i7 8550U | RAM: 13/16 GB | DISK: 424 GB (ext4) | KERNEL: 6.13.2-arch1-1...
WinApps |
WinApps | ❯ Downloading Tiny 11 from archive.org...
WinApps |
WinApps | 0K ........ ........ ........ ........ 0% 3.11M 19m11s
WinApps | 32768K ........ ........ ........ ........ 1% 2.16M 23m12s
WinApps | 65536K ........ ........ ........ ........ 2% 1.51M 28m17s
WinApps | 98304K ........ ........ ........ ........ 3% 1.49M 30m47s
WinApps | 131072K ........ ........ ........ ........ 4% 2.46M 29m4s
WinApps | 163840K ........ ........ ........ ........ 5% 2.86M 27m19s
WinApps | 196608K ........ ........ ........ ........ 6% 1.41M 28m55s
WinApps | 229376K ........ ........ ........ ........ 7% 1.13M 31m16s
WinApps | 262144K ........ ........ ........ ........ 7% 944K 34m13s
.
.
.
BdsDxe: failed to load Boot0002 "UEFI QEMU QEMU HARDDISK " from PciRoot(0x0)/Pci(0xA,0x0)/Scsi(0x0,0x0): Not Found
WinApps | BdsDxe: loading Boot0001 "UEFI QEMU DVD-ROM QM00013 " from PciRoot(0x0)/Pci(0x5,0x0)/Sata(0x0,0xFFFF,0x0)
WinApps | BdsDxe: starting Boot0001 "UEFI QEMU DVD-ROM QM00013 " from PciRoot(0x0)/Pci(0x5,0x0)/Sata(0x0,0xFFFF,0x0)
WinApps | ❯ Windows started succesfully, visit http://localhost:8006/ to view the screen...
You can also view what is happening to Windows OS from a web browser at http://127.0.0.1:8006. It takes some time to update the Windows 11 with latest patches. Once the update process is completed, you must shutdown Windows OS.
Now edit the ~/winapps/compose.yaml file by commentin the following line:
1
comment '- ./oem:/oem'
after commenting, it should look like following:
1
# comment '- ./oem:/oem'
We will use the above config file for booting the Windows OS from now onwards. For this, make the following directory and copy the compose.yaml file to it:
1
2
mkdir -p ~/.config/winapps
cp ~/winapps/compose.yaml ~/.config/winapps/compose.yaml
Finally, ensure to shutdown and boot the Windows OS again:-
1
2
docker compose --file ~/.config/winapps/compose.yaml down
docker compose --file ~/.config/winapps/compose.yaml up
At the moment, it is not possible to access the files stored in different partitions. This will be a problem if you want to save or open a file from different partitions. To overcome this, it is recommended to link the mounted partition to your home directory like
ln -s /mnt/Data /home/username.
Download, Install and Activate MS Office 2011
Once Windows 11 VM is successfully installed, Install MS Office 20XX in client system. I used following method to install MS Office 2011. The post I referred says it is legal to do that. Please let me know if it violates any sort of license, I will remove this section.
Download copy of 2011 to ~/Downloads directory from Linux host.
1
wget https://c2rsetup.officeapps.live.com/c2r/download.aspx\?ProductreleaseID\=ProPlus2021Retail\&platform\=x64\&language\=en-us\&version\=O16GA -P ~/Downloads -O ms_office_setup.exe
Login to Windows 11 and copy ms_office_setup.exe file from Linux file system to Downloads of Windows 11 and start the installation. This is required as *.exe files can be executed only from Windows filesystem.
The activation code shown below is also taken from another of the GitHub repo. Execute all lines of command at one go in the Cmd window with Admin privilege on Windows 11 VM.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
if exist "C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\Office16\ospp.vbs" cd /d "C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\Office16"
if exist "C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Office\Office16\ospp.vbs" cd /d "C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Office\Office16"
for /f %x in ('dir /b ..\root\Licenses16\ProPlus2021VL_KMS*.xrm-ms') do cscript ospp.vbs /inslic:"..\root\Licenses16\%x"
cscript ospp.vbs /inpkey:FXYTK-NJJ8C-GB6DW-3DYQT-6F7TH
cscript ospp.vbs /sethst:kms.msgang.com
cscript ospp.vbs /act
pause
Once MS Office is installed on Windows 11 you must logout.
Configure Winapps
Before installing winapps, we must create a configuration file at ~/.config/winapps/winapps.conf with following content.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
##################################
# WINAPPS CONFIGURATION FILE #
##################################
# INSTRUCTIONS
# - Leading and trailing whitespace are ignored.
# - Empty lines are ignored.
# - Lines starting with '#' are ignored.
# - All characters following a '#' are ignored.
# [WINDOWS USERNAME]
RDP_USER="sundar"
# [WINDOWS PASSWORD]
# NOTES:
# - If using FreeRDP v3.9.0 or greater, you *have* to set a password
RDP_PASS="Pa$$w0rd"
# [WINDOWS DOMAIN]
# DEFAULT VALUE: '' (BLANK)
RDP_DOMAIN=""
# [WINDOWS IPV4 ADDRESS]
# NOTES:
# - If using 'libvirt', 'RDP_IP' will be determined by WinApps at runtime if left unspecified.
# DEFAULT VALUE:
# - 'docker': '127.0.0.1'
# - 'podman': '127.0.0.1'
# - 'libvirt': '' (BLANK)
RDP_IP=""
# [WINAPPS BACKEND]
# DEFAULT VALUE: 'docker'
# VALID VALUES:
# - 'docker'
# - 'podman'
# - 'libvirt'
# - 'manual'
WAFLAVOR="docker"
# [DISPLAY SCALING FACTOR]
# NOTES:
# - If an unsupported value is specified, a warning will be displayed.
# - If an unsupported value is specified, WinApps will use the closest supported value.
# DEFAULT VALUE: '100'
# VALID VALUES:
# - '100'
# - '140'
# - '180'
RDP_SCALE="100"
# [ADDITIONAL FREERDP FLAGS & ARGUMENTS]
# NOTES:
# - You can try adding /network:lan to these flags in order to increase performance, however, some users have faced issues with this.
# DEFAULT VALUE: '/cert:tofu /sound /microphone'
# VALID VALUES: See https://github.com/awakecoding/FreeRDP-Manuals/blob/master/User/FreeRDP-User-Manual.markdown
RDP_FLAGS="/cert:tofu /sound /microphone"
# [MULTIPLE MONITORS]
# NOTES:
# - If enabled, a FreeRDP bug *might* produce a black screen.
# DEFAULT VALUE: 'false'
# VALID VALUES:
# - 'true'
# - 'false'
MULTIMON="false"
# [DEBUG WINAPPS]
# NOTES:
# - Creates and appends to ~/.local/share/winapps/winapps.log when running WinApps.
# DEFAULT VALUE: 'true'
# VALID VALUES:
# - 'true'
# - 'false'
DEBUG="true"
# [AUTOMATICALLY PAUSE WINDOWS]
# NOTES:
# - This is currently INCOMPATIBLE with 'docker' and 'manual'.
# - See https://github.com/dockur/windows/issues/674
# DEFAULT VALUE: 'off'
# VALID VALUES:
# - 'on'
# - 'off'
AUTOPAUSE="off"
# [AUTOMATICALLY PAUSE WINDOWS TIMEOUT]
# NOTES:
# - This setting determines the duration of inactivity to tolerate before Windows is automatically paused.
# - This setting is ignored if 'AUTOPAUSE' is set to 'off'.
# - The value must be specified in seconds (to the nearest 10 seconds e.g., '30', '40', '50', etc.).
# - For RemoteApp RDP sessions, there is a mandatory 20-second delay, so the minimum value that can be specified here is '20'.
# - Source: https://techcommunity.microsoft.com/t5/security-compliance-and-identity/terminal-services-remoteapp-8482-session-termination-logic/ba-p/246566
# DEFAULT VALUE: '300'
# VALID VALUES: >=20
AUTOPAUSE_TIME="300"
# [FREERDP COMMAND]
# NOTES:
# - WinApps will attempt to automatically detect the correct command to use for your system.
# DEFAULT VALUE: '' (BLANK)
# VALID VALUES: The command required to run FreeRDPv3 on your system (e.g., 'xfreerdp', 'xfreerdp3', etc.).
FREERDP_COMMAND=""
The username and password values should be exactly what we have used in compose.yaml file. In my case, I changed only RDP_USER and RDP_PASS fields.
Once the config file is created, we can download and execute the winapps online installer from the host OS i.e., Arch Linux in this case using following command:
1
bash <(curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/winapps-org/winapps/main/setup.sh)
Follow the on-screen instruction. Install winapps to current system is recommended. That’s it.
Now onwards, you can open any Word, Presentation or Excel sheets by right click and choosing appropriate MS Office application names. Anytime, you can access Windows 11 OS from your favourite launchers. For Xfce, it is under Application –> Others –> Windows and on KDE, it is under Lost and Found.
Miscellaneous
I have tried winapps on GNOME, KDE, XFCE and also in Hyprland. I found that performance of MS Office is much better in XFCE and more surprisingly in Hyprland. It opens all application as intended and faster. Whenever you reboot your system, Windows 11 should also be booting in background. If something goes wrong, it is most likely that Windows 11 has not booted in the background. You can use following commands to check and control Windows 11 VM using docker commands.
Check if the Windows 11 is booted by checking docker process.
1
docker ps
and it should show the running process as shown below, if your Windows OS is booted correctly:
1
2
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
4d4e0f472f61 dockurr/windows "/usr/bin/tini -s /r…" 7 minutes ago Up 2 minutes 0.0.0.0:3389->3389/tcp, :::3389->3389/tcp, 0.0.0.0:8006->8006/tcp, 0.0.0.0:3389->3389/udp, :::8006->8006/tcp, :::3389->3389/udp windows
Following actions can be performed whenever you are in need with respect to Windows 11 Virtual Machine.
1
2
3
4
5
6
docker compose --file ~/.config/winapps/compose.yaml start # Power on the Windows VM
docker compose --file ~/.config/winapps/compose.yaml pause # Pause the Windows VM
docker compose --file ~/.config/winapps/compose.yaml unpause # Resume the Windows VM
docker compose --file ~/.config/winapps/compose.yaml restart # Restart the Windows VM
docker compose --file ~/.config/winapps/compose.yaml stop # Gracefully shut down the Windows VM
docker compose --file ~/.config/winapps/compose.yaml kill # Force shut down the Windows VM
That’s all. Happy editing…